Social Status in Ancient Egypt
Posted on 22nd December 2020
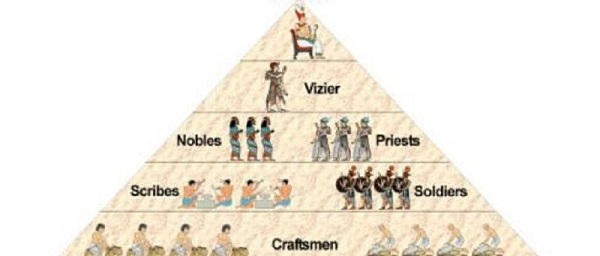
Ancient Egypt had a clear hierarchy with Pharaoh being the ultimate ruler.
Pharaoh
Vizier and other government officials
Priests and Nobles
Scribes
Craftsmen
Farmers, Peasants and Slaves
Within this hierarchy men and women were classed as equal in Ancient Egypt, both could own property, buy and sell merchandise, marry and divorce and take legal action in court. This was unusual at that time as in most ancient countries, women were treated as second class citizens and were subservient to men.
As women had equal rights, they could take up many positions working alongside men, including working in official government, although few took up this opportunity.
Women in their own right could:
Buy, sell and own property such as; land, livestock, servants and slaves.
Take legal action, testify in court, act as a witness and serve on a jury.
Sign contracts.
Work in any position that a man held
Many women from wealthy families still chose to stay at home, whereas poorer women chose to work alongside their husbands in the fields.
Tagged as: Junior Ancient Egypt
Share this post: